General Method of Polymerisation
General Method of Polymerisation: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Addition Polymers, Condensation Polymers, Free Radical Addition Mechanism, Cationic Addition Polymerisation, Types of Polymerisation Reactions, Reaction of Chain Initiation Steps, etc.
Important Questions on General Method of Polymerisation
Which of the following is a condensation polymer?
Polymer formation from monomers starts by:
Which of the following is not correctly matched
Which one of the following polymers is prepared by addition polymerisation?
The copolymer formed by addition polymerization of styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of peroxide is:
A polymer, which finds use in baby feeding bottles:
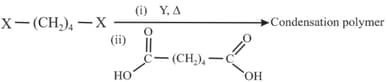
In the above equations, and can be,
(a) , / / Heat
(b) , / / Heat
(c) , / / Heat
Which of the following polymers can be used for lubrication and as an insulator?
Polypropylene is obtained by polymerisation of:
Condensation of diethyl carbonate and bisphenol-A polymerises to form:
Nylon- is:
(a) a condensation polymer
(b) a polyamide
(c) formed by step growth process
Which of the following is not a copolymer?
A polymer used in paints is _______.
Nylon--nylon- is a co-polymer of -aminohexanoic acid and
The major product of the following reaction is _________
Styrene
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization?
A monomer of a polymer upon ozonolysis gives one mole of methylglyoxal and two moles of formaldehyde. Give its free radical mechanism of addition polymerisation.
Which of the following sets contains only addition polymers ?
The monomeric unit of orlon molecule is
The material used as coating for non-stick pans is
